In our sheep dissection lab, we dissected a sheep's brain, taking a closer look at each of external the parts (cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem) as well as the internal parts( pons, medulla oblongata, midbrain, thalamus, hypothalamus, corpus collasum, and optic nerve). Each internal structure within the brain is in charge of a specific part, for example the pons controls involuntary actions like breathing and your pulse). In order to effectively transmit sensory information and messages throughout the body-- we have myelin in our cerebrum, shaped like branches to increase the transmission speed and clarity of the sensory neurons. When we did the Sheep eye dissection, we noticed the optic nerve ending at the back of the eye. Click this link to see more about that post: Sheep Eye Dissection. Here in the brain we also see the optic nerve, which transfers the visual information from the retina to the brain.
The picture below shows our pinned points of the external structures including markings for the anterior (white pin) and the posterior (red black pin) sides.
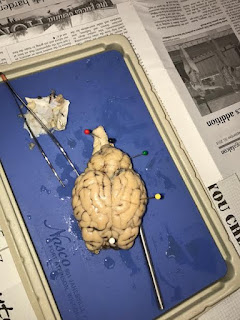 |
External View of Brain with pinned structures
(cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem)
|
 |
| Sketch of External View of Brain |
- Yellow pin: Cerebrum; controls the emotional and higher functions such as thought, emotion, and action
- Green pin: Cerebellum regulates voluntary movement and receives sensory neurons through myelin
- Red pin: Brain stem; controls involuntary functions and transmits sensory messages between brain and rest of body
After observing the external brain, we sliced the brain in half down the midline to see the cross-section internal parts. We saw the cerebrum contained a vein-like structure called myelin. These help to increase the speed in transmitting sensory neurons faster through cerebellum. In the picture below, we pinned specific parts of the brain that were visible with the medial cut.
 |
| Medial View of Internal Brain with pinned structures
(pons, medulla oblongata, midbrain, thalamus,
hypothalamus, corpus collasum, optic nerve)
|
 |
| Sketch of Medial View of Internal Brain |
- Flat Metal Pin: Pons; relays messages from cortex and cerebellum
- White: Medulla Oblongata; controls involuntary actions
- Blue: Thalamus; transmits sensory messages to the cortex, cerebellum, and medulla and correlates consciousness
- Yellow: Midbrain; consists of the Thalamus and Hypothalamus, essential part of Central Nervous System
- Black: Hypothalamus: essential part of connecting nervous system to endocrine system
- Red: Corpus Collasum; connects the left and right hemispheres and allows both sides to connect and communicate
- Green: Optic Nerve: Transmits visual information from the retina to the brain
Finally, we made a cross-section of the medial plane, exposing the white matter versus the grey matter.
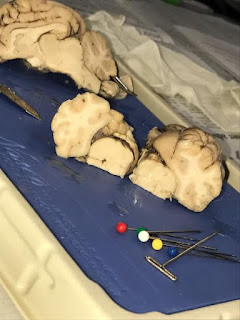 |
| White Matter vs. Grey Matter |
 |
| Sketch of White Matter vs Grey Matter |


No comments:
Post a Comment